
Contact Us: +86-15508631887(WhatsApp/WeChat)
Email:sales@finerchem.com
|
Production Methods |
Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone is synthesized commercially from either of the bitter-flavanones neohesperidin or naringin by catalytic hydrogenation under alkaline conditions in a process first described in the 1960s, in which neohesperidin is purified by recrystallization from water solutions.Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone is obtained by the alkaline hydrogenation of neohesperidin. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Insoluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Neosperidin dihydrochalcone is a ether-alcohol derivative. The ether being relatively unreactive. Flammable and/or toxic gases are generated by the combination of alcohols with alkali metals, nitrides, and strong reducing agents. They react with oxoacids and carboxylic acids to form esters plus water. Oxidizing agents convert alcohols to aldehydes or ketones. Alcohols exhibit both weak acid and weak base behavior. They may initiate the polymerization of isocyanates and epoxides. |
|
Fire Hazard |
The flash point of Neosperidin dihydrochalcone has not been determined, but Neosperidin dihydrochalcone is probably combustible. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Notclassified |
|
Pharmaceutical Applications |
Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone is a synthetic intense sweetening agent approximately 1500–1800 times sweeter than sucrose and 20 times sweeter than saccharin. Structurally it is an analogue of neohesperidin, a flavanone that occurs naturally in Seville oranges (Citrus aurantium). Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone is used in pharmaceutical and food applications as a sweetening agent and flavor enhancer. The sweetness profile is characterized by a lingering sweet/menthol-like aftertaste.The typical level used in foods is 1–5 ppm although much higher levels may be used in certain applications such as chewing gum. Synergistic effects occur with other intense and bulk sweeteners such as acesulfame K, aspartame, polyols, and saccharin. In pharmaceutical applications, neohesperidin dihydrochalcone is useful in masking the unpleasant bitter taste of a number of drugs such as antacids, antibiotics, and vitamins. In antacid preparations, levels of 10–30 ppm result in improved palatability. |
|
Safety |
Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone is accepted for use in food products either as a sweetener or flavor modifier in a number of areas including Europe, USA, Australia, New Zealand, and several countries in Africa and Asia. It is also used in a number of oral pharmaceutical formulations. Animal toxicity studies suggest that neohesperidin dihydrochalcone is a nontoxic, nonteratogenic, and noncarcinogenic material at the levels used in foods and pharmaceuticals.In Europe, an acceptable daily intake of 0–5 mg/kg body-weight has been established. |
|
storage |
Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone is stable for over three years when stored at room temperature. Accelerated stability studies on aqueous solutions stored at 30–60°C and pH 1–7 for 140 days indicate that neohesperidin dihydrochalcone solutions are likely to be stable for 12 months at room temperature and pH 2–6.Solutions formulated with some or all of the water replaced by solvents with a lower dielectric constant are reported to have longer shelf-lives. The bulk material should be stored in a cool, dry, place protected from light. |
|
Definition |
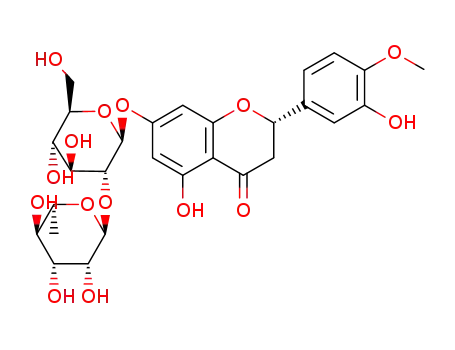
ChEBI: A member of the dihydrochalcones that is 3,2',4',6'-tetrahydroxy-4-methoxydihydrochalcone attached to a neohesperidosyl residue at position 4' via glycosidic linkage. It is found in sweet orange. |
|
General Description |
Off-white crystals or powder. Insoluble in water. |
InChI:InChI=1/C28H36O15/c1-11-21(34)23(36)25(38)27(40-11)43-26-24(37)22(35)19(10-29)42-28(26)41-13-8-16(32)20(17(33)9-13)14(30)5-3-12-4-6-18(39-2)15(31)7-12/h4,6-9,11,19,21-29,31-38H,3,5,10H2,1-2H3/t11-,19+,21-,22+,23+,24-,25+,26+,27-,28+/m0/s1
The invention discloses a preparation me...
C32H46O15

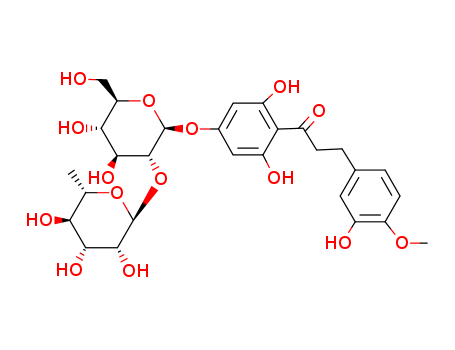
neohesperidin
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hydrogenchloride; In water; pH=6; pH-value; Reagent/catalyst; Industrial scale;
|
96.8% |
C30H42O16


neohesperidin
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With citric acid; pH=7; Reagent/catalyst; pH-value; Industrial scale;
|
97.2% |
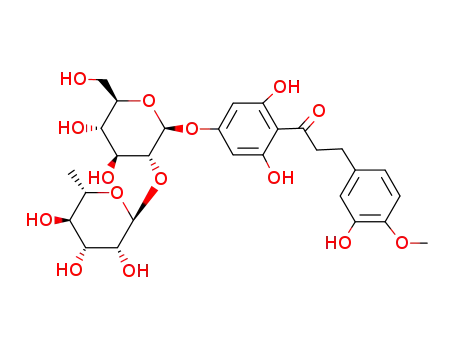
neohesperidin
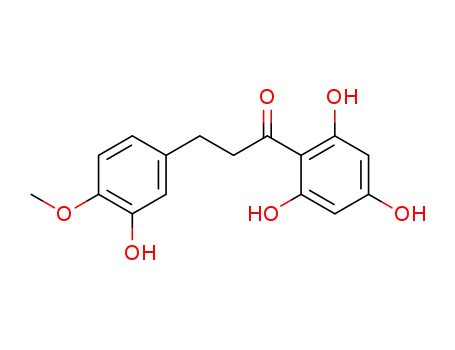
3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxy-phenyl)-1-(2,4,6-trihydroxyphenyl)propan-1 -one
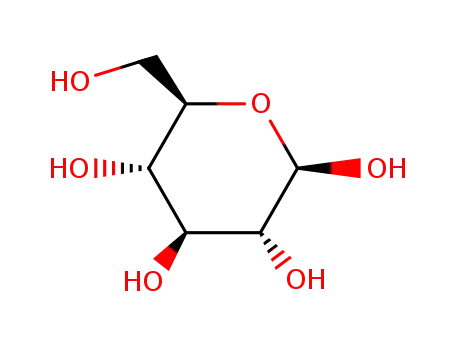
β-D-glucose
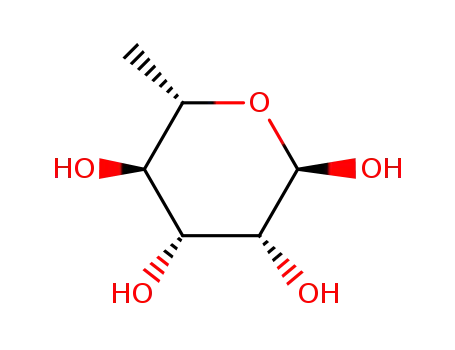
L-rhamnose
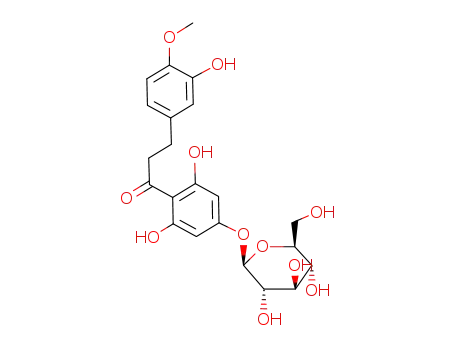
hesperetin dihydrochalcone-4'-β-D-glucoside
