
Contact Us: +86-15508631887(WhatsApp/WeChat)
Email:sales@finerchem.com
|
Industrial and Commercial Uses |
Widely used in various industries, including pH control, cleaning agents, metal processing, textile dyeing and tanning, adhesives, and water treatment. |
|
Medical and Cosmetic Applications |
Utilized in the pharmaceutical industry as a skin care agent, and in the food industry as a flavor and preservative. |
|
Biomedical Applications |
Used in medical applications for its ability to convert to biodegradable polymers like polyglycolic acid (PGA) and copolymers such as polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA). PLGA is used in various medical applications due to its good mechanical properties. |
|
Regulatory Status |
Previously regulated as an antimicrobial pesticide under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), but its use as a pesticide has been cancelled. |
|
General Description |
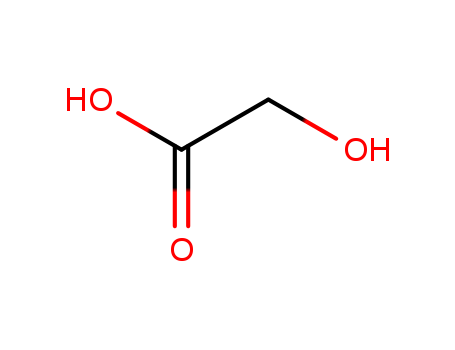
Glycolic acid is a type of alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) derived from sugar cane. It is a colorless, odorless, and water-soluble chemical that is commonly used in skin care products. Glycolic acid is known for its exfoliating properties, as it works by breaking down the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting the shedding of the outer layer of the skin. This process helps to improve skin texture, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and even out skin tone. Additionally, glycolic acid can also help to unclog pores and reduce acne. It is a popular ingredient in chemical peels and other professional skin treatments, as well as in over-the-counter skincare products such as cleansers, toners, and serums. While glycolic acid can be beneficial for many skin types, it is important to use it cautiously and always wear sunscreen when using products containing this ingredient, as it can increase skin sensitivity to the sun. |
InChI:InChI=1/C2H4O3/c3-1-2(4)5/h3H,1H2,(H,4,5)/p-1
At formic acid concentrations of about 0...
Screening for microorganisms oxidizing e...
-
Density functional theory calculations d...
In this study, the electrochemical reduc...
The electrochemical oxidation of diclofe...
Various processes for preparing aldaric ...
The starch used to enhance the paper sur...
L-Tartaric acid
carbon dioxide

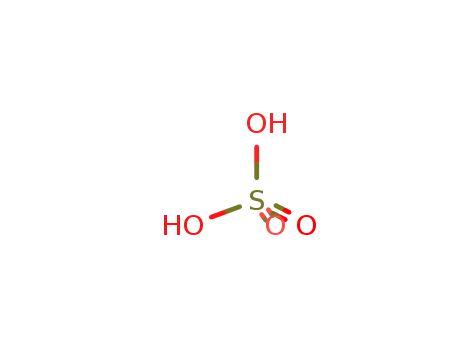
sulfuric acid

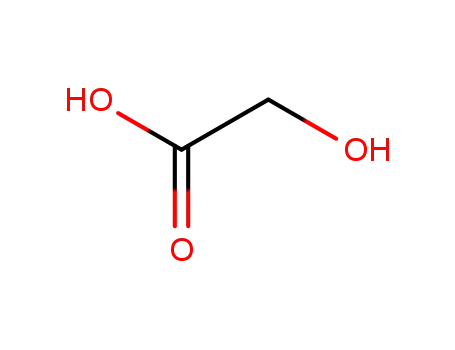
glycolic Acid

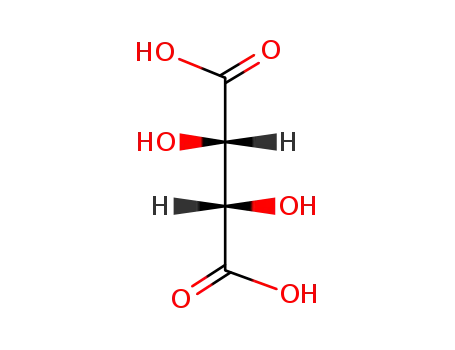
DL-tartaric acid

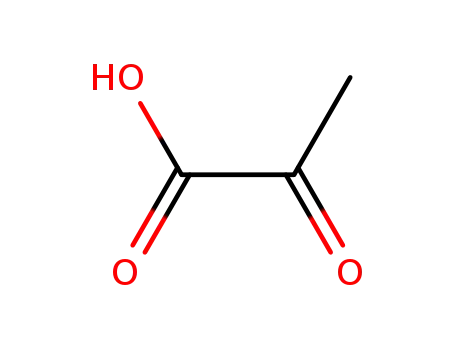
2-oxo-propionic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|
rhodamine B

phenylacetic acid


glycolic Acid

LACTIC ACID

propylene glycol

cyclohexen-1-ol

1.3-butanediol

4-Methyl-1-pentanol

terephthalic acid

Phthalic acid dibutyl ester

2-Phenylbutyric acid

cyclohexanol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
for 0.5h; pH=5; UV-irradiation; Darkness;
|
tetrachloromethane
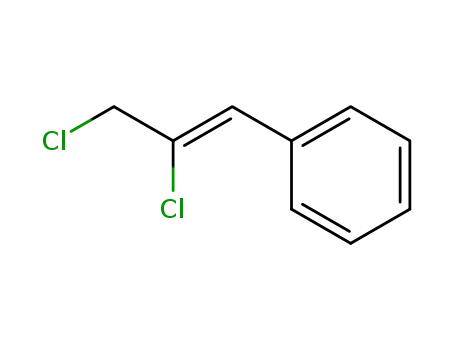
(Z)-1,2-dichloro-3-phenyl-2-propene
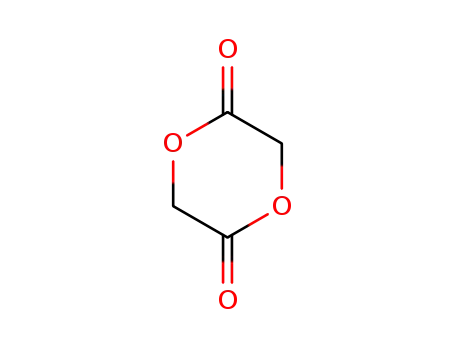
glycolide
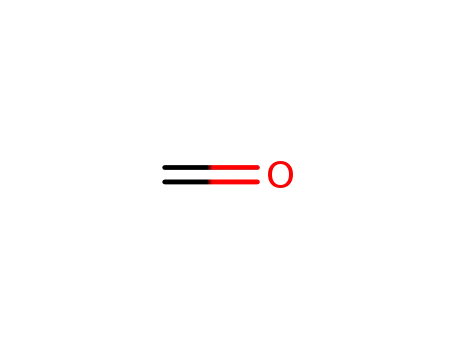
formaldehyd
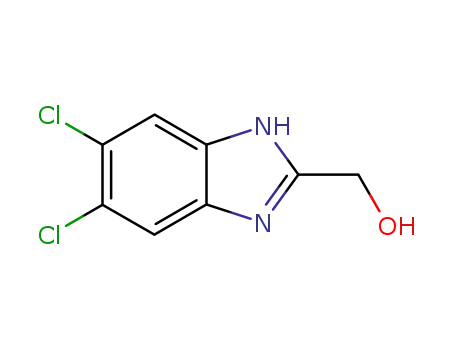
5,6-dichloro-2-hydroxymethyl-1H-benzimidazole
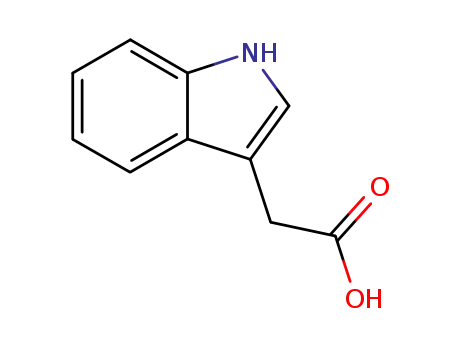
indole-3-acetic acid
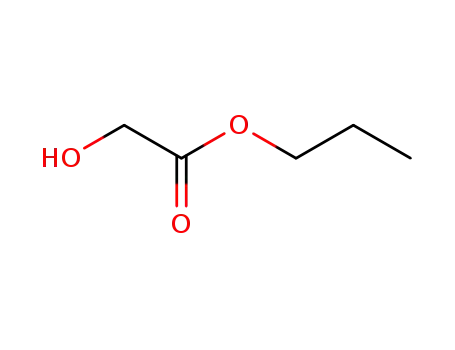
n-propyl 2-hydroxyacetate
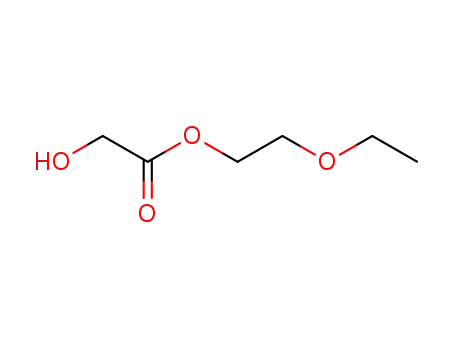
glycolic acid-(2-ethoxy-ethyl ester)
