
Contact Us: +86-15508631887(WhatsApp/WeChat)
Email:sales@finerchem.com
|
Preparation |
The preparation of Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate is as follows:To a monoester sodium salt solution were added 2g of N, N-dimethylformamide, 1g of pyridine, 1g of triethylamine,Cooling to -5~0°C, 60g diphosgene was slowly added dropwise within 1.5h dropwise addition was complete, warmed to room temperature (25°C), incubated for 2h, the reaction was allowed to stand after filtration, washing organic solution. Dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, the solvent was distilled off at atmospheric pressure to give crude product 65~70g. After cooling and crystallization, 57-60g of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate were obtained in a yield of 60-63%. |
|
Reactions |
The reaction of substituted anilines with Boc2O in the presence of a stoichiometric amount of 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) in an inert solvent (acetonitrile, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, tetrahydrofuran, toluene) at room temperature leads to aryl isocyanates in almost quantitative yields within 10 min.Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate and 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine revisited. Their reactions with amines and alcohols |
|
Hazard |
An irritant that may cause serious eye injury; May cause skin sensitization; Highly toxic by inhalation |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Flammable |
|
Purification Methods |
Melt the ester by heating at ~35o, and distil it in a vacuum. If IR and NMR ( 1810m 1765 cm-1 , in CCl4 1.50 singlet) suggest very max impure, then wash with an equal volume of H2O containing citric acid to make the aqueous layer slightly acidic, collect the organic layer and dry it over anhydrous MgSO4 and distil it in a vacuum. [Pope et al. Org Synth 57 45 1977, Keller et al. Org Synth 63 160 1985, Grehn et al. Angew Chem 97 519 1985.] FLAMMABLE. |
|
Used in Organic Synthesis |
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate is used as a protecting group reagent to introduce the tert-butoxycarbonyl (BOC) group onto amine functionalities, allowing for selective modification of molecules during organic synthesis. [3] |
|
Used in Pharmaceutical Industry |
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate is employed in the pharmaceutical industry for the synthesis of various drug intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredients. It serves as a versatile reagent for introducing protective groups and functionalizing molecules in drug synthesis processes. |
|
Used in Chemical Research |
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate finds application in chemical research as a reagent for the modification of amines, alcohols, and thiols. Its use in various synthetic transformations enables the study of new reaction pathways and the synthesis of novel compounds. [1] [2] |
|
Used in Environmental Remediation |
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate is utilized in environmental remediation processes, particularly in the reduction of pollutants such as hexavalent chromium in contaminated soil. Its reductive properties make it effective in converting toxic compounds into less harmful forms. |
|
Used in Food Science |
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate is employed in food science for the synthesis of flavor compounds and food additives. Its role in introducing specific functional groups allows for the customization of flavors and enhancement of food products. |
|
Specification |
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (Boc2O) is a versatile reagent widely used in organic synthesis, particularly for introducing the tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) protecting group in peptide chemistry and other transformations. It serves as an efficient activating agent for esterification reactions, enabling the coupling of carboxylic acids and alcohols under mild conditions with minimal byproducts. Additionally, Boc2O is employed in the synthesis of heterocycles, such as pyrrolidines and lactams, where it aids in protecting amines or facilitating key cyclization steps. Its utility extends to biocatalytic processes and the preparation of bioactive molecules, demonstrating broad functional group compatibility and ease of purification due to volatile byproducts (CO2 and t-butanol). |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate is an acyclic carboxylic anhydride. It is functionally related to a dicarbonic acid. |
|
General Description |
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (Boc2O) is a reagent mainly used for the introduction of the Boc protecting group to amine functionalities. It is also used as a dehydrating agent in some organic reactions, particularly with carboxylic acids, certain hydroxyl groups, or with primary nitroalkanes. |
InChI:InChI=1/C10H18O5/c1-8(2,3)11-7(10)12-9(4,5)6/h1-6H3
Three diazabicyclo analogs of BMS-378806...
The invention discloses a method for syn...
The invention relates to a preparation m...
Tert-butyl pyrocarbonate is an important...
The invention relates to novel thiophene...
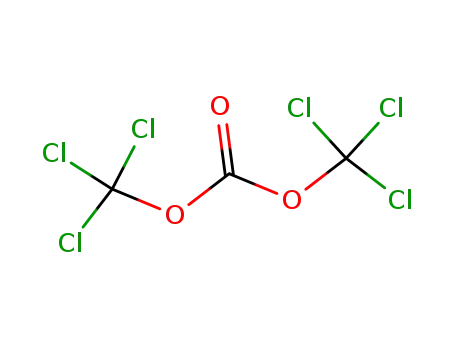
bis(trichloromethyl) carbonate
tert-butyl alcohol

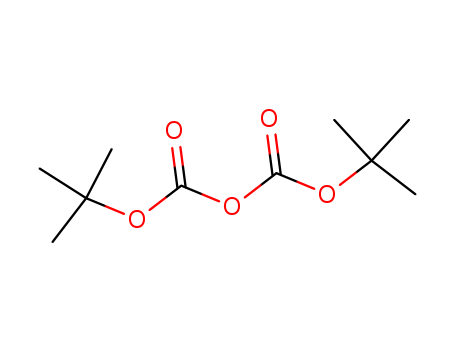
di-tert-butyl dicarbonate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
bis(trichloromethyl) carbonate; tert-butyl alcohol; With triethylamine; In hexane; at -5 ℃;
With sodium hydroxide; In hexane; water; at 10 ℃; for 5.33333h; Reagent/catalyst; Temperature;
|
72% |
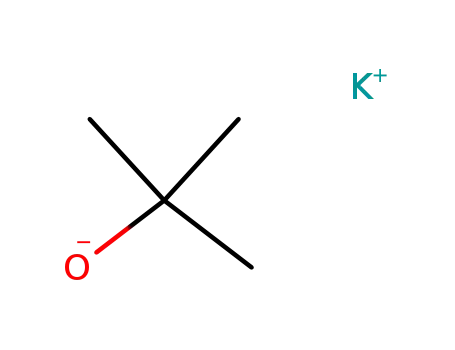
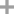
potassium tert-butylate

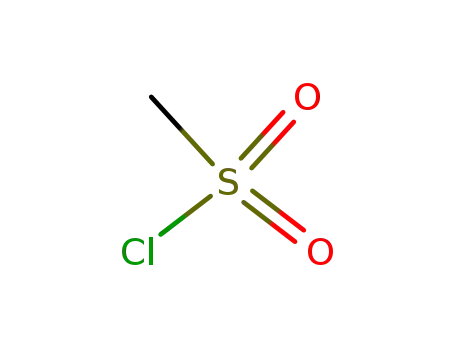
methanesulfonyl chloride

di-tert-butyl dicarbonate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With pyridine; sulfuric acid; sodium hydrogencarbonate; In hexane; water;
|
89% |
|
In hexane; water;
|
87% |
|
In water; N,N-dimethyl-formamide; toluene;
|
24% |
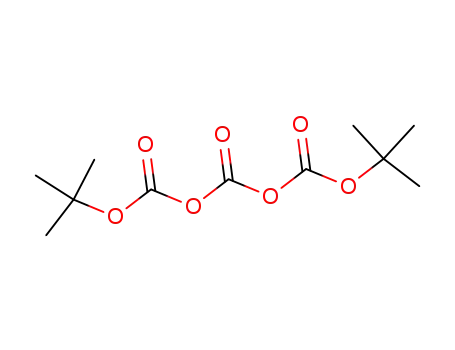
di-tert-butyl tricarbonate
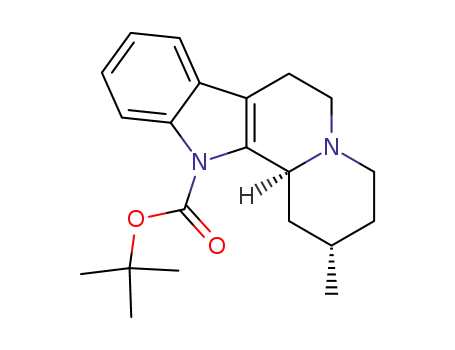
(2S,12bS)-2-Methyl-1,3,4,6,7,12b-hexahydro-2H-indolo[2,3-a]quinolizine-12-carboxylic acid tert-butyl ester
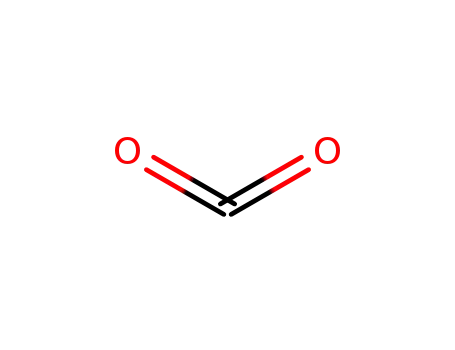
carbon dioxide

potassium tert-butylate
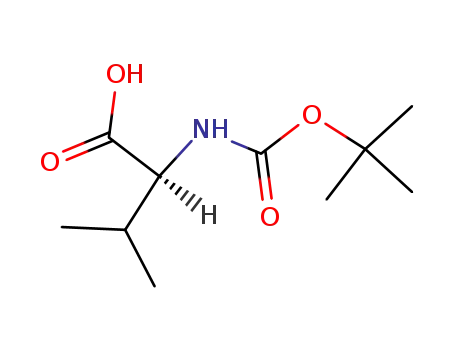
t-Boc-L-valine
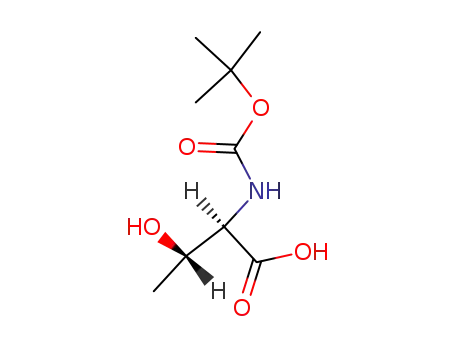
(2R,3S)-2-tert-butoxycarbonylamino-3-hydroxybutyric acid
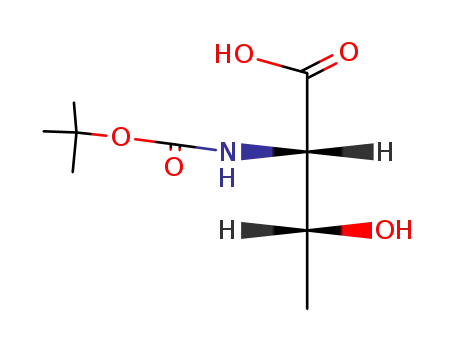
Boc-Thr-OH
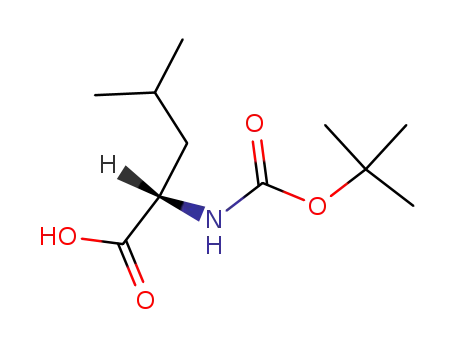
N-tert-butoxycarbonyl-L-leucine
