
Contact Us: +86-15508631887(WhatsApp/WeChat)
Email:sales@finerchem.com
|
Chemical Description |
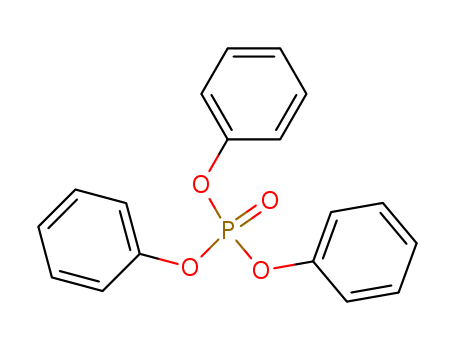
Triphenyl phosphate is an ester of phosphoric acid with three phenyl groups attached to the phosphate group. |
|
Preparation |
Triphenyl phosphate is prepared by reacting phosphorus pentoxide and phenol (Budavari, 2001), or by reacting phosphorus oxychloride and phenol (Snyder, 1990). On a larger scale phosphorus oxychloride and phenol are reacted in an esterification tank with heating. The HCL formed is trapped and condensed, while the crude triphenyl phosphate runs into a large tank where it is purified. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Organophosphates, such as Triphenyl phosphate, are susceptible to formation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides. |
|
Hazard |
Toxic by inhalation. Cholinesterase inhibitor. Questionable carcinogen. |
|
Health effects |
Non-industrial:An allergic reaction in a 67-year old woman to spectacle frames containing triphenyl phosphate was reported. Patch tests with analytical grade triphenyl phosphate in that individual indicated a reaction at concentrations as low as 0.05%. This observation was confirmed in another male patient (Carlsen et al 1986).Industrial:Occupational exposure of men engaged in manufacturing triphenyl phosphate produced a statistically significant reduction in erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase activity and plasma cholinesterase activity. There was no evidence of adverse clinical effects in men exposed to triphenyl phosphate for as long as 10 years. Exposure was to triphenyl phosphate mist, vapor, and dust at a weighted average air concentration of 3.5 mg/m3 (Sutton et al 1960). |
|
Fire Hazard |
Noncombustible solid. Incompatibility— none. |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by subcutaneous route. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Absorbed slowly, particularly by skin contact. Not a potent cholinesterase inhibitor. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of POx. See also TRITOLYL PHOSPHATE. |
|
Potential Exposure |
Triphenyl phosphate is used to impregnate roofing paper and as a fire-resistant plasticizer in plastics; for cellulose esters in lacquers and varnishes. Used in making adhesives, gasoline additives; flotation agents; insecticides, surfactants, antioxidants, and stabilizers. A substitute for camphor. |
|
Source |
Triphenyl phosphate was identified as a component in outer covers of brand-new computer video display units. Concentrations were estimated to be 8 to 10 and 0.3 to 0.5 wt % in 4 and 6 video display units, respectively. The concentrations of triphenyl phosphate in the remaining 8 video display units were <0.02 wt % (Carlsson et al., 2000). |
|
Environmental fate |
Chemical/Physical. When an aqueous solution containing triphenyl phosphate (0.1 mg/L) and chlorine (3 to 1,000 mg/L) was stirred in the dark at 20 °C for 24 h, the benzene ring was substituted with one to three chlorine atoms (Ishikawa and Baba, 1988). The reported hydrolysis half-lives at pH values of 8.2 and 9.5 were 7.5 and 1.3 d, respectively (Howard and Doe, 1979). Decomposes at temperatures greater than 410 °C (Dobry and Keller, 1957) |
|
Metabolism |
Rat liver microsomal enzymes degraded triphenyl phosphate in the presence of NADPH, but also in the absence of NADPH. The product of incubation was diphenyl phosphate. It was clear that the reaction was cytochrome P-450-linked since the reaction was inhibited by carbon monoxide (Sasaki et al 1984). Goldfish liver microsomes metabolized only about 10% of triphenyl phosphate (Sasaki et al 1985). Houseflies treated with triphenyl phosphate were analyzed after 24 h and the presence of diphenyl p-hydroxyphenyl phosphate was confirmed (Eto et al 1975). |
|
Shipping |
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required. |
|
Purification Methods |
Crystallise the phosphate from EtOH or pet ether (b 60-80o)/EtOH. [Cox & Westheimer J Am Chem Soc 80 5441 1958, Krishnakumar & Sharma Synthesis 558 1983, Cherbuliez in Organo Phosphorus Compounds (Kosolapoff & Maier eds) Wiley Vol 6 pp 211-577 1973, Beilstein 6 III 658, 6 IV 720.] |
|
Toxicity evaluation |
Triphenyl phosphate(TPP) is neurotoxic, causing paralysis at high dosages. Like tri-o-cresyl phosphate (TOCP), it is a cholinesterase inhibitor. The acute oral toxicity is low. The acute toxicity via subcutaneous administration is low to moderate. The toxic symptoms from high dosages in test animals were tremor, diarrhea, muscle weakness, and paralysis.LD50 value, oral (mice): 1320 mg/kgLD50 value, subcutaneous (cats): 100 mg/kgCleveland et al. (1986) investigated the acute and chronic toxicity to various species of freshwater fish of phosphate ester compounds containing TPP. The adverse toxic effects occurred at exposure concentrations of 0.38–1.0 mg/L. |
|
Incompatibilities |
Incompatible with strong oxidizers; strong acids; nitrates may cause fire or explosions. Phosphates are incompatible with antimony pentachloride, magnesium, silver nitrate, zinc acetate. |
|
Waste Disposal |
Incinerate in furnace equipped with alkaline scrubber. |
|
General Description |
Triphenyl phosphate (TPP) is a triaryl phosphate compound synthesized catalytically from white phosphorus and phenols under aerobic conditions using iron catalysts and iodine, offering an environmentally friendly alternative by avoiding chlorine-based processes and acid waste generation. The synthesis is optimized for high selectivity and full conversion, with reaction progress and product composition monitored via advanced analytical techniques such as 31P NMR, HPLC-MS, and GC-MS. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: Triphenyl phosphate is an aryl phosphate resulting from the formal condensation of phosphoric acid with 3 mol eq. of phenol. It has a role as a flame retardant and a plasticiser. It is functionally related to a phenol. |
|
Application |
Triphenyl Phosphate is used in the insecticidal composition. It is also use in hydraulic liquids, and adhesives, inks, coatings, as a plasticizer in lacquers and varnishes, and as a substitute for camphor in celluloid materials to make the latter stable and fireproof. |
InChI:InChI=1/C18H15O4P/c19-23(20-16-10-4-1-5-11-16,21-17-12-6-2-7-13-17)22-18-14-8-3-9-15-18/h1-15H
The combination of a catalytic amount of...
We have studied the spectral composition...
The factor responsible for the deactivat...
We describe the synthesis of an ionic-li...
The electrochemical characteristics of r...
Various dialkyl chlorophosphates are pre...
-
The application of iodosobenzene (1) and...
The reaction of ozone with triphenyl pho...
Abstract: The possibility of controlling...
-
The synthesis and characterization of se...
Pyridine accelerated the decomposition o...
Triaryl phosphates were prepared by a "o...
The hypofluorous acid acetonitrile compl...
-
The reduction of phosphorus acid chlorid...
Various types of trivalent phosphorus co...
The reaction of phosphoryl chloride with...
-
This paper presents a new synthetic rout...
Industrially important triaryl phosphite...
A method for preparing phosphate ester d...
Flow synthesis techniques have received ...
C26H35O9P3S2

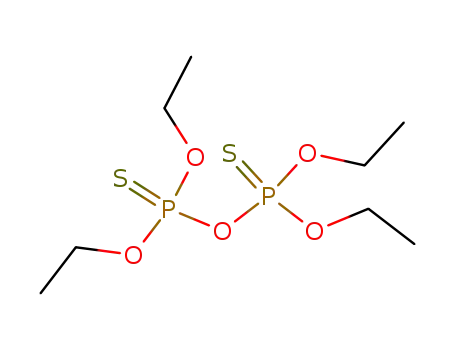
sulfotep
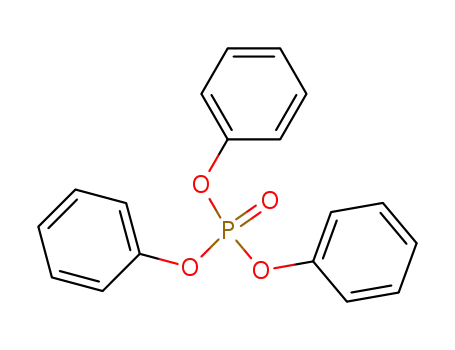
phosphoric acid triphenyl ester

C22H25O6P2S(1+)*C4H10BF3O3PS(1-)
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With boron trifluoride diethyl etherate; at -80 - -60 ℃; Product distribution;
|
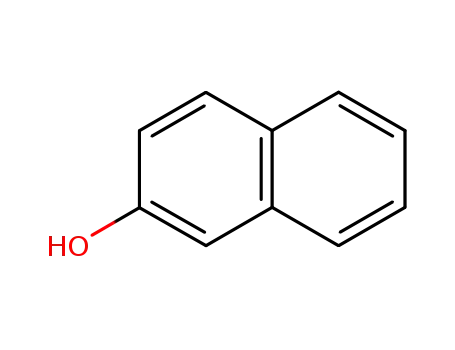
β-naphthol

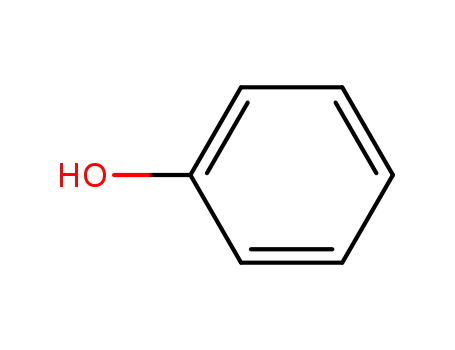
phenol


phosphoric acid triphenyl ester

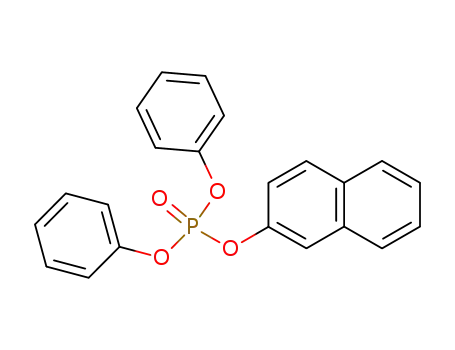
naphthalen-2-yl diphenyl phosphate

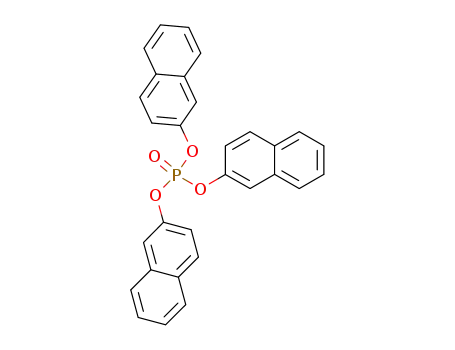
tri(naphthalen-2-yl) phosphate

![phosphoric acid di-[2]naphthyl ester-phenyl ester](/upload/2025/4/e18af229-b477-404a-807a-e054487c1a82.png)
phosphoric acid di-[2]naphthyl ester-phenyl ester
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
β-naphthol; With trichlorophosphate; magnesium chloride; at 120 ℃; for 2h;
phenol; In toluene; at 160 ℃; for 5h; under 150.015 Torr;
|
|
|
β-naphthol; With trichlorophosphate; aluminum (III) chloride; at 120 ℃; for 2h;
phenol; In toluene; at 160 ℃; for 5h; under 150.015 Torr;
|
|
|
β-naphthol; With trichlorophosphate; aluminum (III) chloride; at 150 - 165 ℃; for 8h;
phenol; at 190 - 200 ℃; for 9h;
|
triphenyl phosphite
bromobenzene
diphenylether
diphenyl sulfite
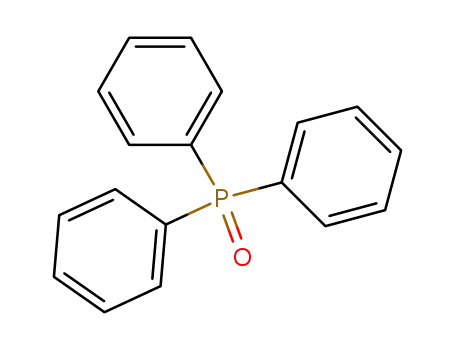
Triphenylphosphine oxide

phenol
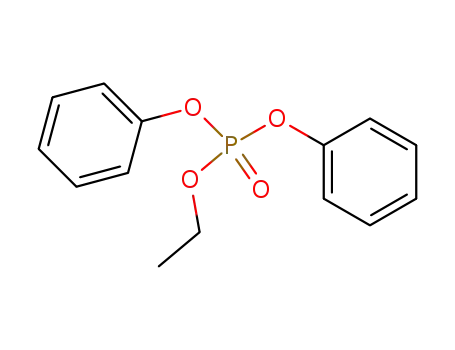
ethyl diphenyl phosphate
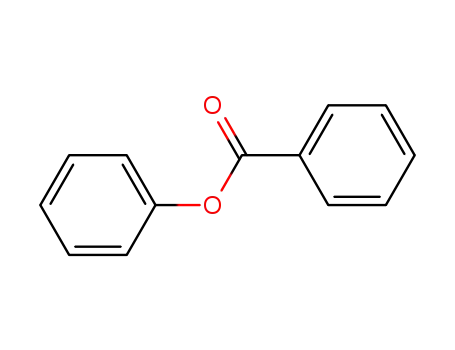
benzoic acid phenyl ester
