
Contact Us: +86-15508631887(WhatsApp/WeChat)
Email:sales@finerchem.com
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Guanidine thiocyanate is a denaturing agent and is used routinely in RNA isolation. It is used as a storage buffer for whole blood samples. Guanidine thiocyanate inactivates nucleases and is ideal for storing and freezing fecal samples for DNA studies. It is used in combination with phenol?chloroform in RNA extraction. |
|
Toxicity evaluation |
Guanidine thiocyanate is used commercially as a disinfectant and a general protein denaturant but its more common use is in the extraction of DNA and RNA in molecular biology. Нere are no reports of guanidine thiocyanate toxicity from oral ingestion. Toxicity of di??erent thiocyanate compounds other than guanidine thiocyanate has been described. Potassium thiocyanate was used over 50 years ago for the treatment of hypertension and its toxicity appears to cause a neurological disorder consisting of generalized weakness, delirium and a decrease level of consciousness. Reports of thiocyanate toxicity from nitroprusside use for hypertension in the setting of renal impairment/failure have also been reported as thiocyanate is renally cleared. In a fatal deliberate ingestion of a herbicide which contained ammonium thiocyanate and aminotriazole, a 54 year old man presented with coma and cardiovascular collapse although the relative contributions of the two herbicides to the clinical toxicity is unknown. |
|
Hazard |
Irritant. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Notclassified |
|
General Description |
Guanidine thiocyanate (also known as isothiocyanic acid, compd. with guanidine (1:1)) is a chemical compound studied for its transport behavior through immobilized liquid membranes, particularly in the presence of crown ethers. Research indicates that its transport efficiency is influenced by the lipophilicity of crown ethers, with more lipophilic variants enhancing flux and membrane stability. The process involves diffusion-limited transport, where partition coefficients and complexation constants play critical roles, and dynamic complexation-decomplexation occurs during diffusion. |
InChI:InChI=1/C2H4N4S/c3-1-7-6-2(4)5/h(H4,4,5,6)
Thermal decomposition of thiourea in a m...
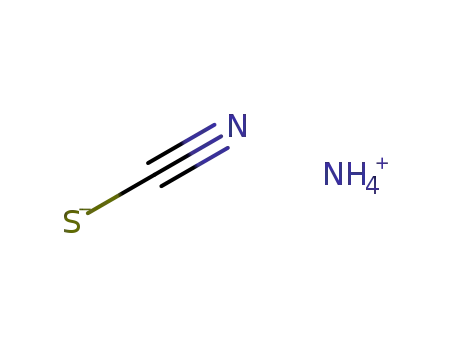
ammonium thiocyanate
dicyandiamide

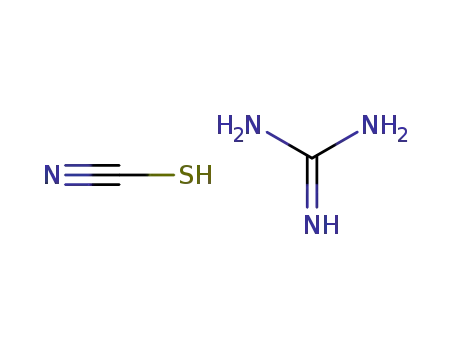
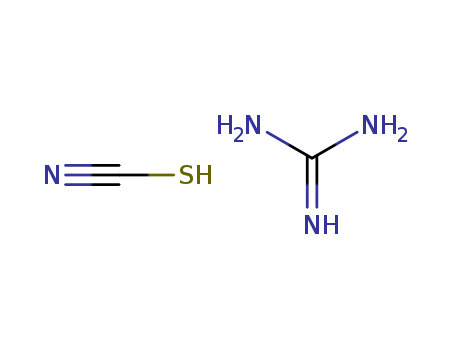
guanidinium thiocyanate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In melt; 55 part of dicyanodiamide reacted with 100 part of NH4SCN;
|
90% |
|
In melt; 55 part of dicyanodiamide reacted with 100 part of NH4SCN;
|
90% |

ammonium thiocyanate


guanidinium thiocyanate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
heating over temp. of formation of (NH4)2CS;
|
|
|
byproducts: NH3, CS2; 220°C;
|
|
|
With ammonia; ammonium chloride; 300°C;
|
25-30 |
|
With ammonia; lead(II) chloride; 300°C;
|
<95 |
|
In neat (no solvent); 20 h at 180-190°C; melt extd. with water; evapn.; crystn.;
|
|
|
heating over temp. of formation of (NH4)2CS;
|
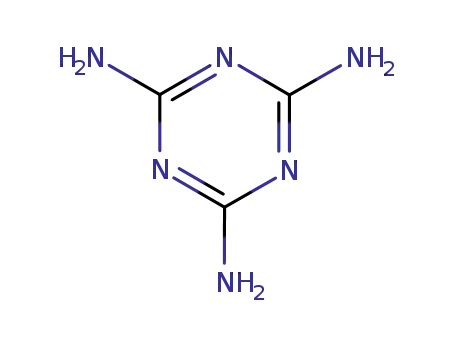
2,4,6-triamino-s-triazine
ammonium thiocyanate
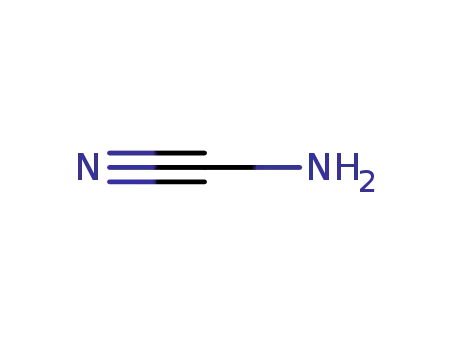
CYANAMID
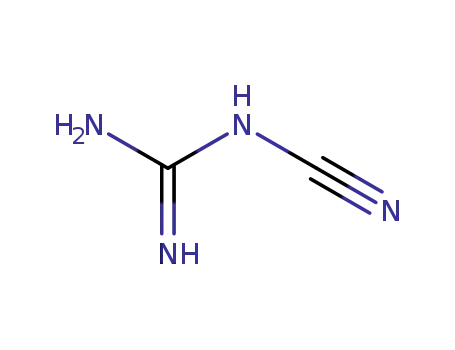
N-Cyanoguanidine
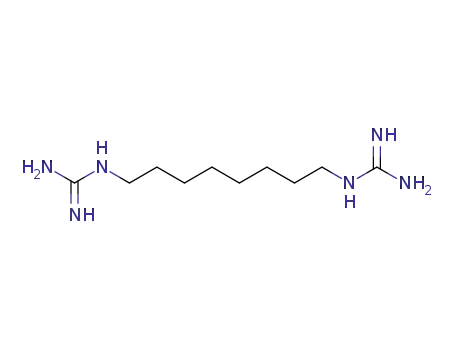
1,8-Diguanidino-octan
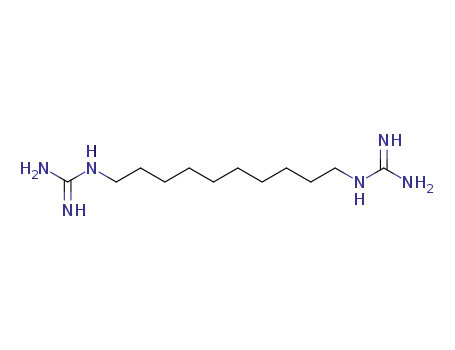
N,N'''-1,10-decanediylbisguanidine
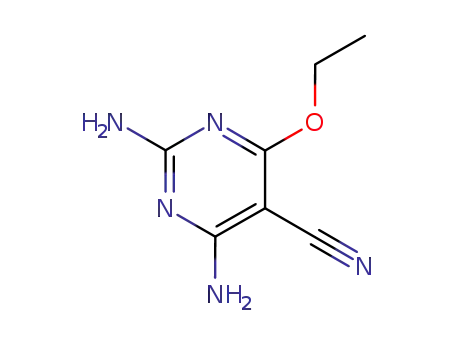
2,4-Diamino-6-ethoxy-5-cyan-pyrimidin
N-carbamimidoyl-N'-phenethyl-thiourea
